Compass, protractor, ruler, scissors, poster board, calculator.
![]() Supplies:
Supplies:
Compass, protractor, ruler, scissors, poster board, calculator.
Activity.
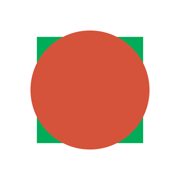
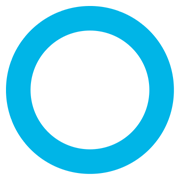
From the poster board make a circle 10 cm in diameter. Cut out from it another circle having 1/2 of the total area (and the same center). You will have a smaller circle and an outer ring. (If you cut the ring, fasten it back together with Scotch tape.) Finally, make a square that has the same area as the small circle.
You will have three figures that have the same area but look differently.
 |
 |
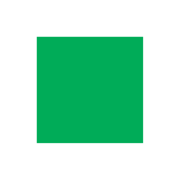 |
(See pictures above.) Find the length of the border of each one. (Remember that the border of the ring consists of two circles, the inside one and the outside one.) Write down the results.
Solution.
Variables and formulas.
| d = 10 cm | diameter of the big circle |
| A = |
area of the small circle, the ring, and the square |
| s = |
side of the square |
| S = 4* |
border of the square |
| r = |
radius of the small circle (because A = |
| C = 2 * |
border (circumference) of the circle |
| R = C + |
border of the ring |
Here is the computation, using the TI-108 calculator.
Keystrokes:
| Keystrokes: | Answers: |
| [3.14] [*] [25] [/] [2] [M+] | A = 39.25 sq. cm |
| [ |
s = 6.3 cm |
| [*] [4] {=] | S = 25.1 cm |
| [MRC] [/] [3.14] [=] [ |
r = 3.5 cm |
| [*] [2] [*] [3.14] [=] | C = 22.2 cm |
| [+] [31.4] [=] | R = 53.6 cm |
Construction.
Draw and cut out the required figures. Be precise!Formulate your observations
"For example, place the center of the circle on top of the center of the square.